Healthcare software development refers to the process of creating, designing, testing, and implementing software applications specifically tailored for use in the healthcare industry. These software solutions are intended to enhance medical processes, improve patient care, streamline administrative tasks, and facilitate efficient data management within healthcare organizations.
Healthcare software development encompasses a wide range of applications and systems, some of which include:
Electronic Health Records (EHR) and Electronic Medical Records (EMR) systems: These applications store and manage patient medical records electronically, making it easier for healthcare providers to access patient information securely and in real-time.
Practice Management Software: These systems help medical practices manage administrative tasks like appointment scheduling, billing, and patient registration.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring: Telemedicine software enables remote consultations between healthcare providers and patients, while remote monitoring software allows healthcare professionals to track patient health data remotely.
Medical Imaging Software: This category includes applications used for processing and analyzing medical images, such as X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and ultrasounds.
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): These software tools assist healthcare providers in making better clinical decisions by providing evidence-based insights and recommendations.
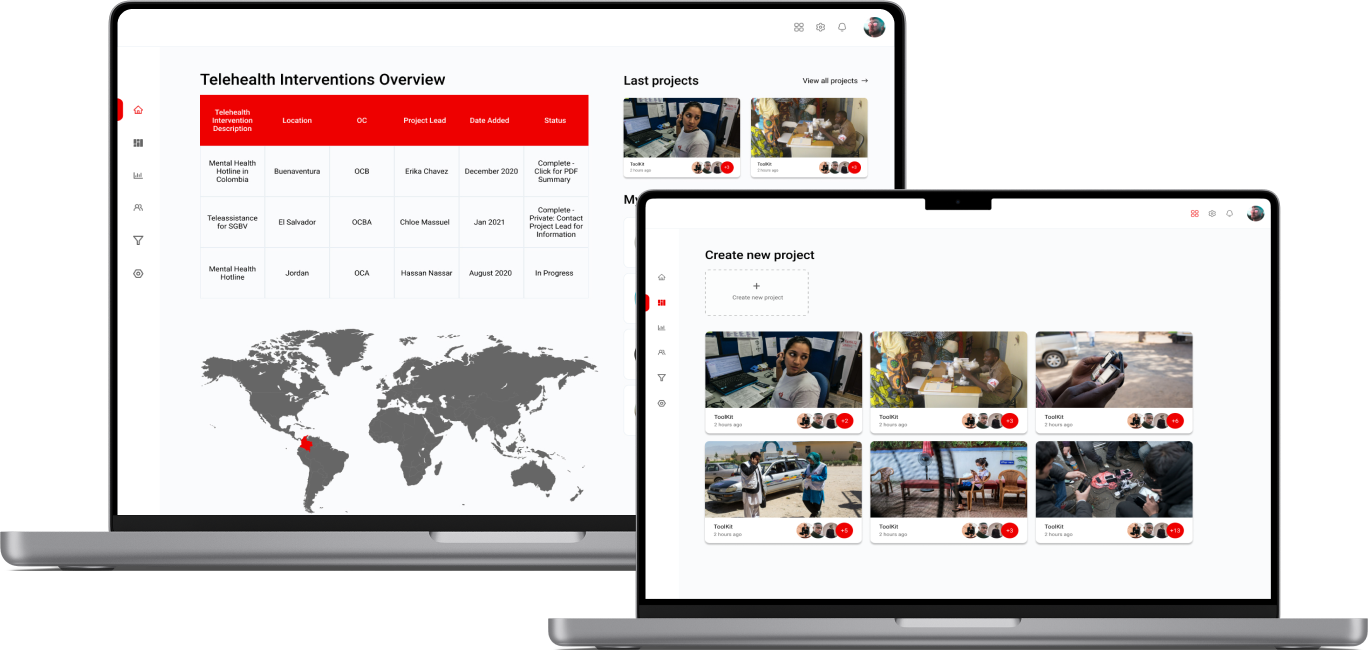
Health Information Exchange (HIE): HIE software allows the secure sharing of patient health information between different healthcare organizations, improving coordination of care.
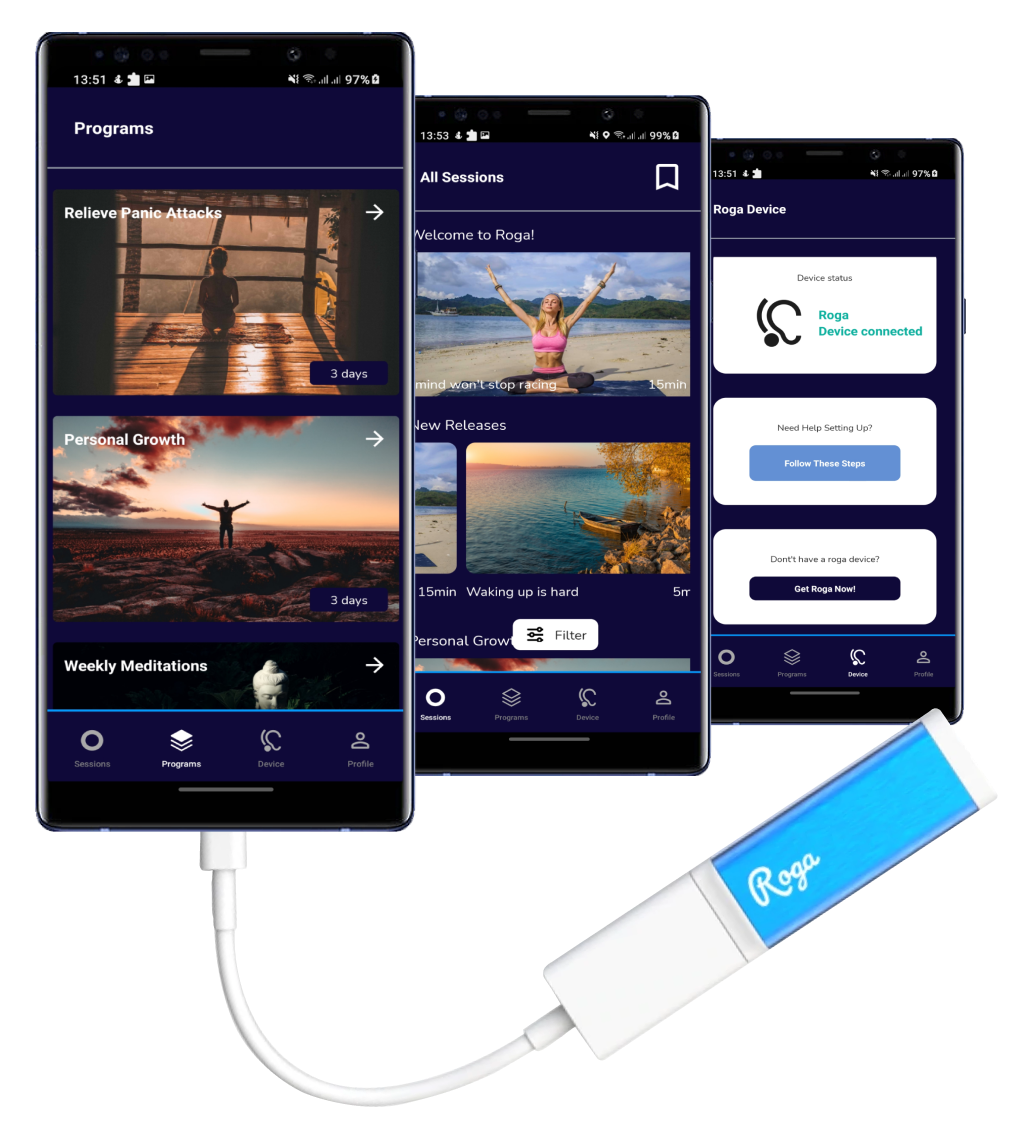
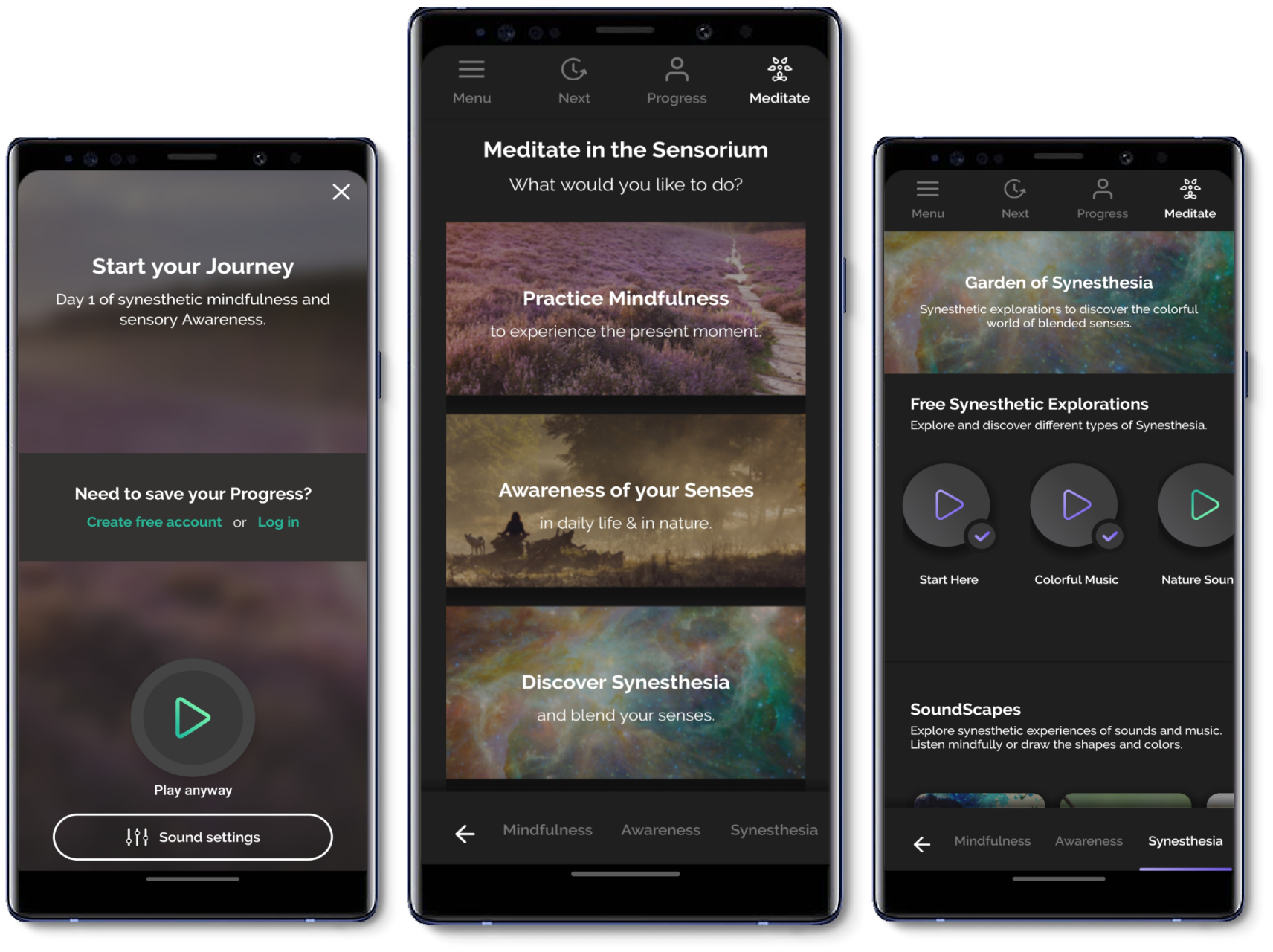
Patient Portals and Mobile Health Apps: These applications enable patients to access their health records, communicate with healthcare providers, schedule appointments, and manage their health.
Healthcare software development is subject to strict regulatory requirements, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the United States, which aim to protect patient privacy and data security. Additionally, developers need to follow industry best practices to ensure the reliability, accuracy, and usability of these critical applications.
The healthcare software development field is constantly evolving due to advancements in technology, and it plays a vital role in transforming the healthcare industry, improving patient outcomes, and enhancing the overall quality of care provided to patients.
DevOps as a ServiceDevOps on autopilot
CTO as a ServiceStregthen your team
Software testingEnsure software quality
Discovery phasePlan your priduct from a to z
Cloud ServicesGeneral information about healthcare cloud services
Google Cloud ServicesEnsuring confidentiality when working with medical systems
AWS Cloud ServicesServices specially designed for the healthcare industry
Microsoft Cloud ServicesPlatform processing, analyzing and sharing medical data